fungi life cycle pdf
Ad Browse Discover Thousands of Science Book Titles for Less. - Asexual - Sporangia produces haploid spores.

3 Life Cycle Of A Heteroecious Macrocyclic Rust Fungus Melampsora Download Scientific Diagram
Section 213 Reproduction in Fungi p.

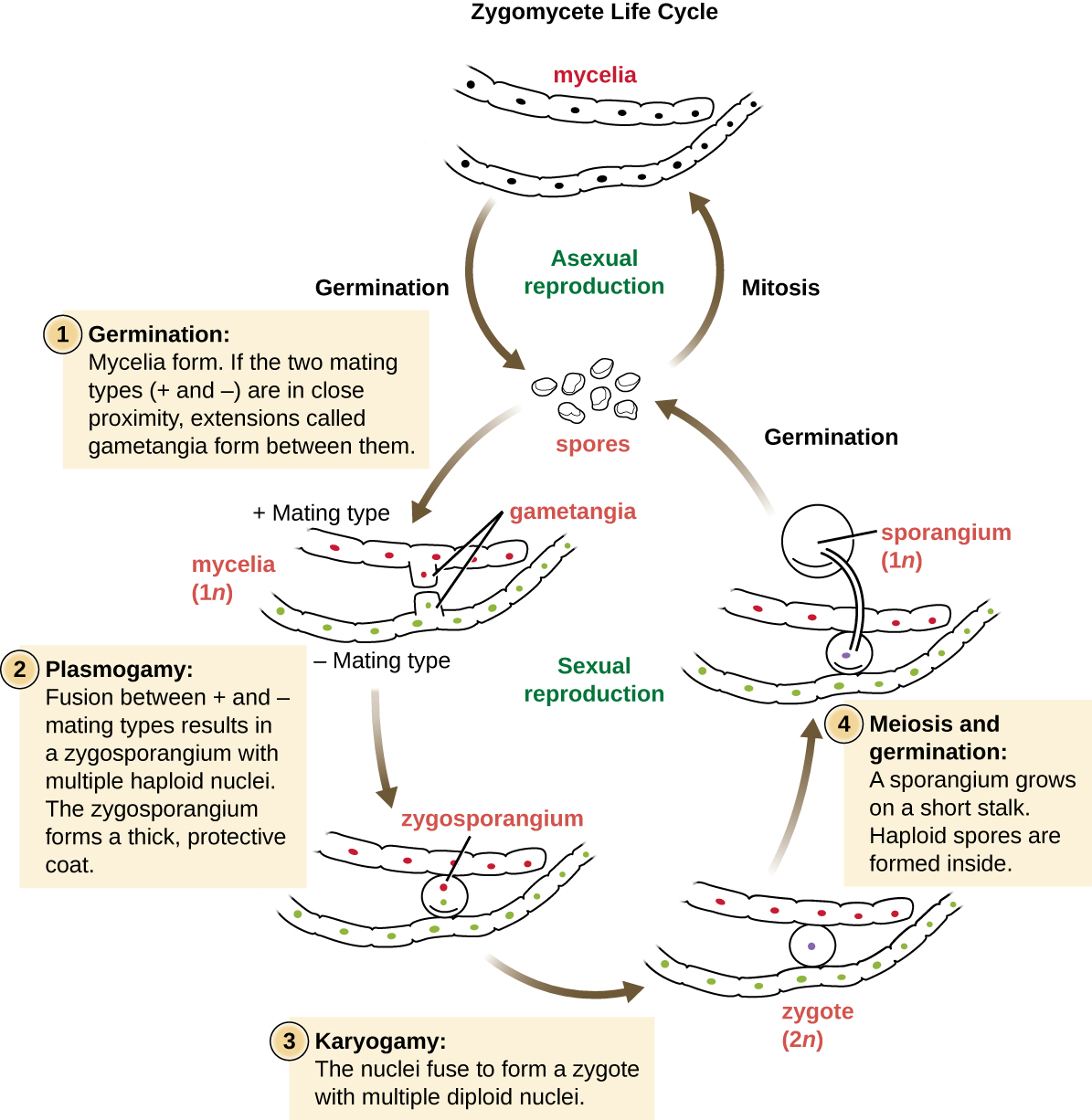
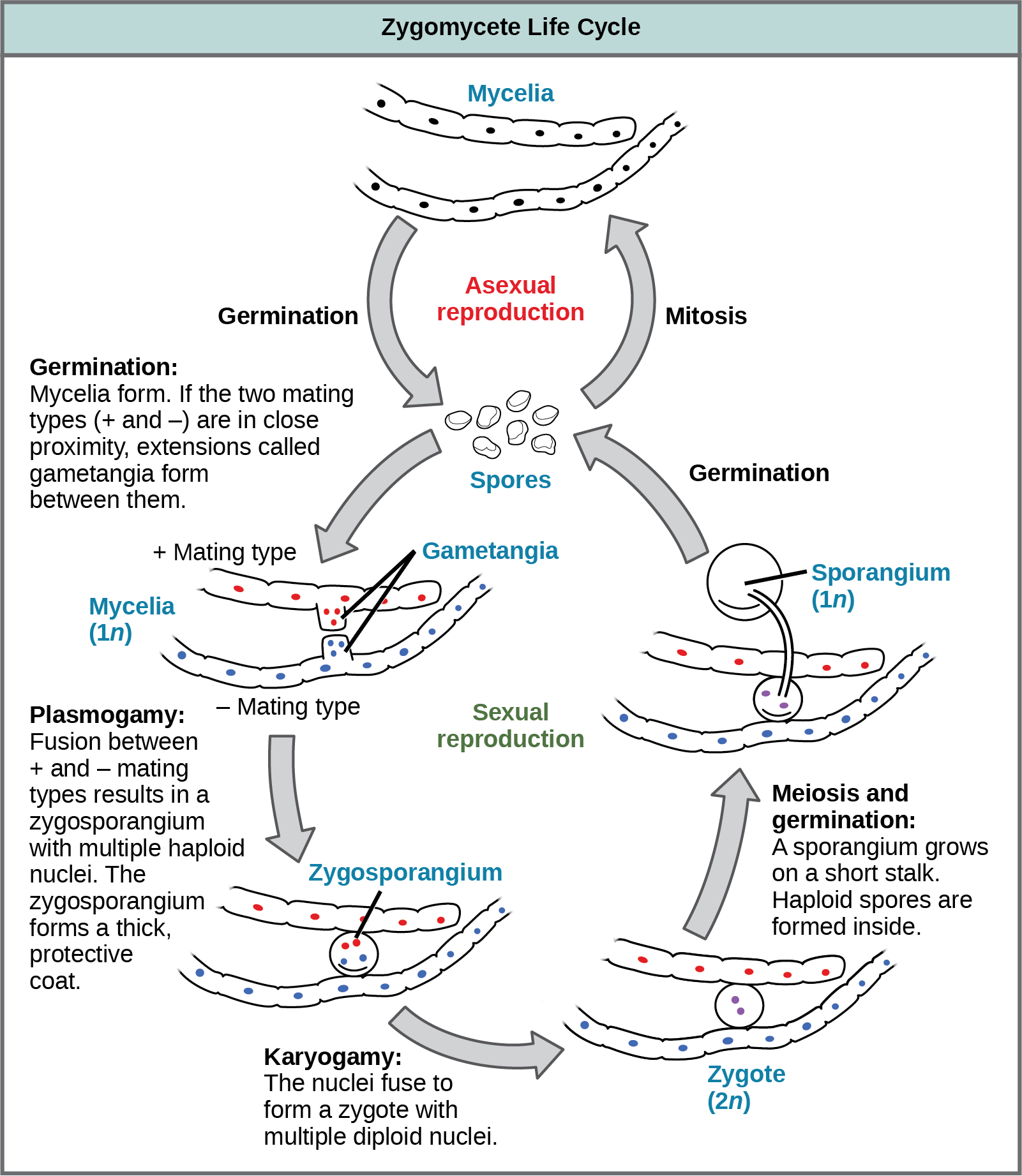
. Some reproduce only sexually others only asexually. Model organisms for biochemical and genetic studies. Their tips swell to produce a sporangium.
Pollination renews the orchids life cycle for the next generation. Individuals are formed without the production of. All fungi begin their life cycle in this stage.
How many species of fungi exist. These are called sporangiophores. - Asexual - Sporangia produces haploid spores.
Each spore will grow into a new hypha and mycelium if it lands on a suitable substrate. The basidiospores germinate and grow into short. Life Cycle of Fungi.
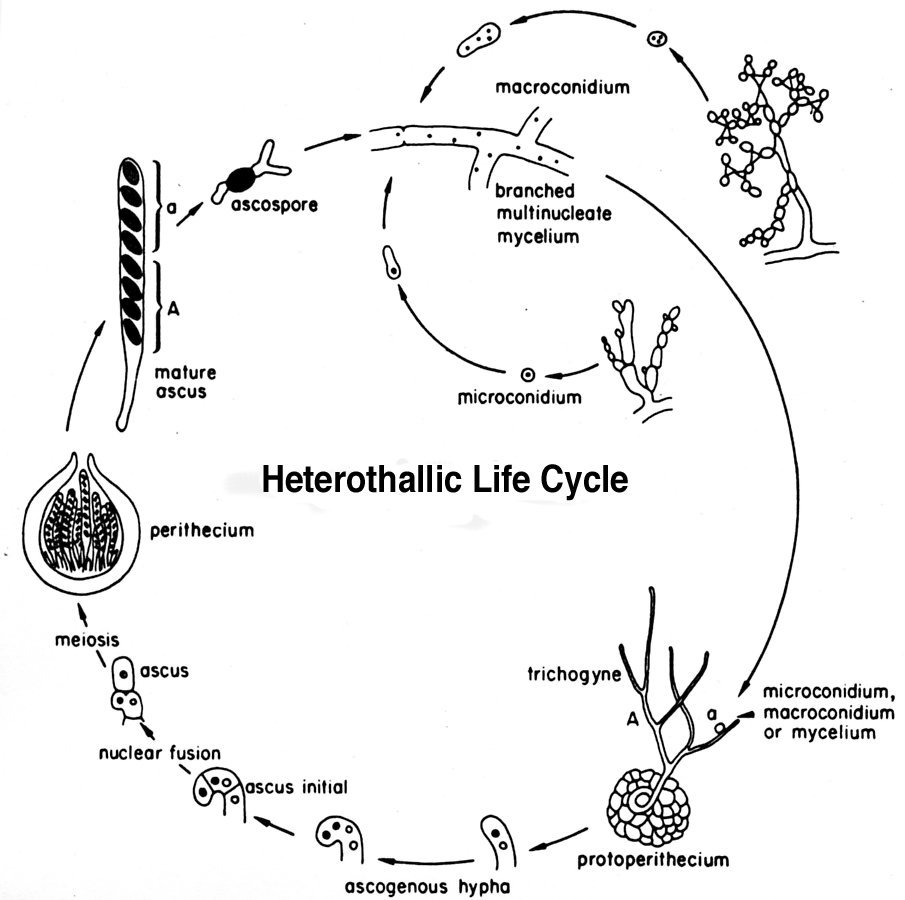
Eight ascospores per ascus sac 5. While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. Evolution Characteristics and Life Cycle Author.
Life Cycle of Fungi. Which letters are haploid diploid and nursing. Fungi life cycle pdf Saturday February 26 2022 Edit.
All about spores and how they work in your garden ecosystem to help. 80000 species of fungi described 1700 new species described each year Estimating the number of fungal species Hawksworth DL. Chytridiomycetes zygomycetes glomeromycetes ascomycetes and basidiomycetes Describe the body plan of a fungus.
Mushrooms have an unusual life cycle. The basidiospores are ejected and. Bernice Speer Last modified by.
Studies on endophytic fungi started nearly two hundred years ago when Person 1772 8 described the species Sphaeria typhinia now called as Epichloe typhinia pers Tul. Plant organs as some point in their life cycle without carrying apparent harm to their host as well as remained internal pathogen in the endophyte category 7. Reproduction is by budding of yeast cells.
Fungi Each orchid life stage is dependent on specific fungi but very few of these fungi have been identified because they rarely form fruiting bodies mushrooms. Fungi life cycle pdf Thursday May 26 2022 Edit. Candida albicans ascomycete is an asexual animal pathogen.
Bernice Speer Created Date. Kulat breeding cycle. Not a true phylum not a natural group.
Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. Fungi Learning Objectives By the end of this unit a student should be able to List distinguishing characteristics describe a typical life cycle and give examples of each of the following fungal groups. By hitching a ride on another organism or even the wind these spores can travel great.
These spores migrate far distances through air by grabbing on to other organisms on the way. Spore Haploid The spore phase is the initial stage of the fungal life cycle. Fungi with no known sexual.
While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. This is similar to sperm and eggs which are similar to human sex cells. Mushroom Yeasts can be used to make bread and alcohols such as wine and beer anaerobic respiration C 6H 12O 6 2C 2H 5OH 2CO 2 Ethanol Baker Brewer Note.
Many lichen fungi too. Life cycle of fungi. Classifications Of Fungi Biology 2e.
Asexual reproduction via conidia F. Generalized life cycle Of fungi. These spores migrate far distances through air by grabbing on to other organisms on the way.
Can be used to produce drugs antibiotics alcohol acids food eg fermented products mushrooms. Beneficial Effects of Fungi Decomposition - nutrient and carbon recycling. Most fungi causing systemic infections are dimorphic.
Pollination renews the orchids life cycle for the next generation. The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Introduction To Fungi Complete Life Cycle Of The Lichen Fungus Calopadia Puiggarii Pilocarpaceae Ascomycetes Documented In Situ Propagule Dispersal Establishment Of Symbiosis Thallus Development And Formation Of Sexual And Asexual Reproductive.
Copy link Link copied. Kulat breeding cycle. Deuteromycetes - fungi imperfecti 1.
Most of the molds indoors are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. Cycles in fungi beginning with relatively simple life cycles Please realize that each of the major groups of fungi has a diversity of life cycles beyond those listed here. How fungi are different from plants and actually are a lot more like animals this includes you.
The CO 2 produced by yeast causes the dough to rise - the heat evaporates the ethanol. - Asexual - Sporangia produces haploid spores. Reproduction is by budding of yeast cells.
The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. This is the first stage in the life cycle of a fungus. In the beginning all spores are haploid which means that they have only a single copy of their entire genetic material.
Filamentous fungi possess a yeast-like phase at some point in their life cycle. The whole life cycle of wood-loving macro-fungi from mushroom back around to mushroom. After spores are released from mature fruit-.
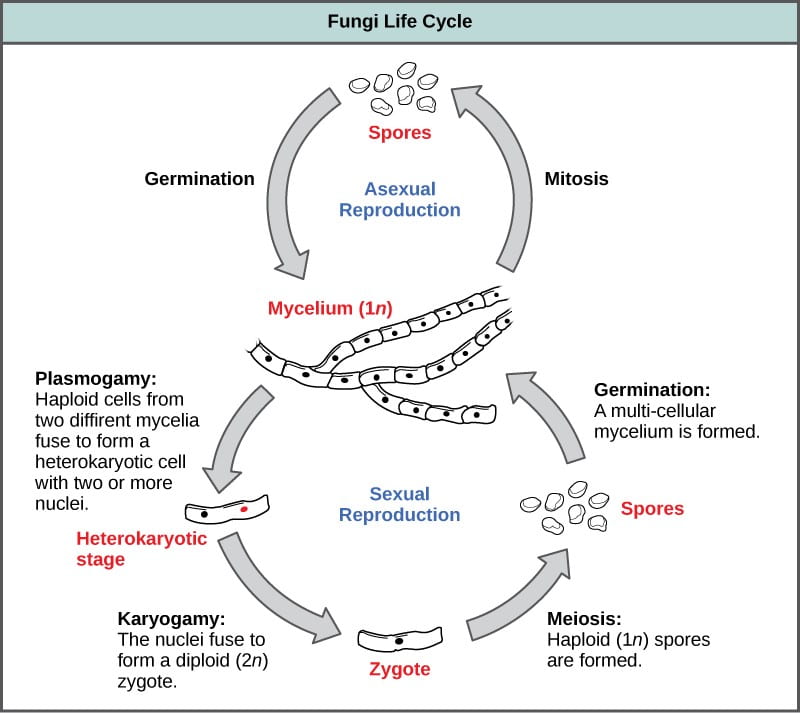
Ecological role Evolution of Animals April 12 2019 Haploid n General Fungal Life Cycle Heterokaryotic Diploid 2n PLASMOGAMY fusion of cytoplasm Heterokaryotic stage. Are chemoheterotrophs require organic compounds for both carbon and energy sources and fungi lack chlorophyll and are therefore not autotrophic. Kulat breeding cycle.
This Russula is a rare exception an orchid mycorrhizal fungus that produces mushrooms. It is the t ype of r eproduction which involves the so matic portion of the fungal thallu s where new. Kulat breeding cycle.
Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. This tutorial illustrates the relationships among these phases in the life cycle of a mushroom. Fertile layer with asci 4.
Fungi early in their lives. Ascomycota - Life cycle 1. Manybut not allfungi reproduce both A Figure 315 sexually and asexually.
Systemic mycosis Primary pathogens Opportunistic pathogens Use of Antibiotics Use of steroids. The basidiospores are ejected and. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
Fungi inhabit almost every place in the environment and humans are exposed to these organisms in various fields of life. Generalized life cycle Of fungi. Lived haploid mycelia O When mature.
Fungi part 2 Review General Fungal Life Cycle Mating types Plasmogamy Karyogamy structures Major groups of fungi What is a lichen. Histoplasma capsulatum Blastomyces dermatidis. Therefore we are going to look at the life cycle of a fungi in asexual and sexual stage.
All fungi start as haploid spores which means they only have one copy of their genetic information. Economic importance of fungi Beneficial fungi Fungi can be used as a source of food eg. Harmful Effects of Fungi Destruction of food lumber paper and cloth.
Kulat breeding cycle. How fungi establish themselves and how you can help make this happen in your garden.
Classifications Of Fungi Biology 2e

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Basidiomycota Life Cycle Study Com
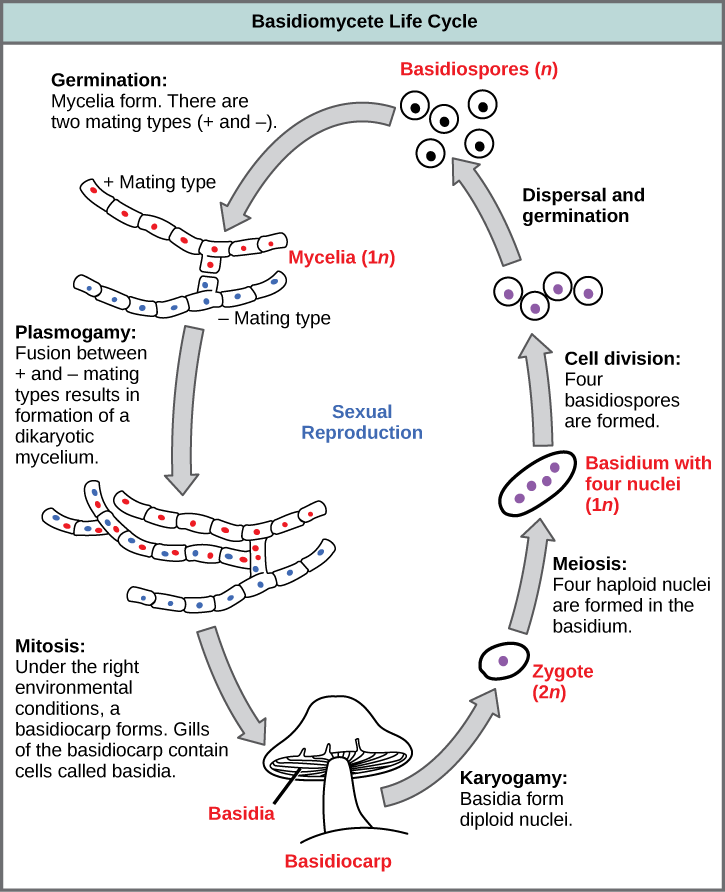
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Diagram Of Monocyclic Yellow And Polycyclic Yellow And Blue Fungi Download Scientific Diagram

Life Cycle Of Penicillium Sp Download Scientific Diagram
Fungi General Characteristics Classification Morphology Pathogenecity
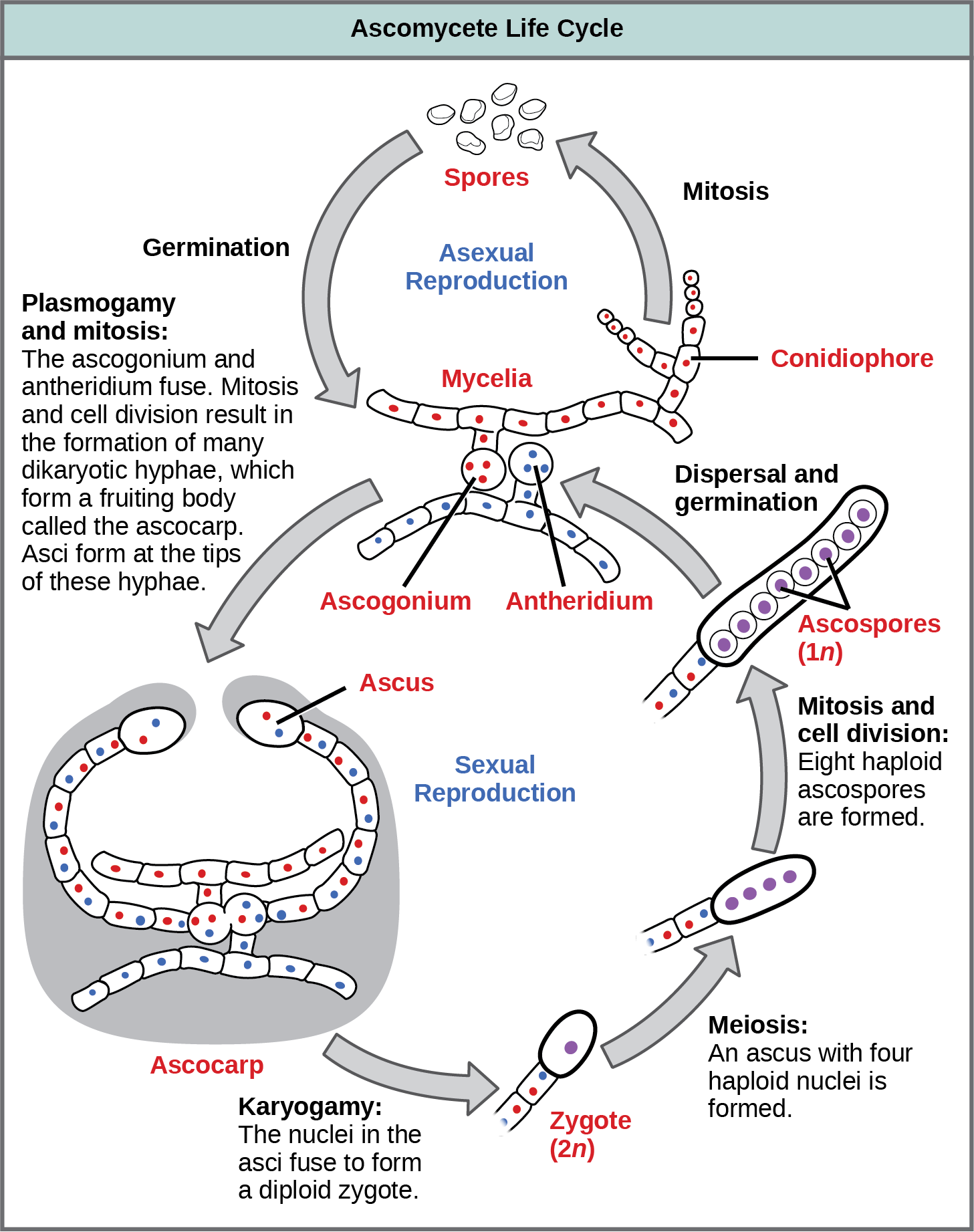
Classifications Of Fungi Biology 2e

Mushroom Life Cycle Kidspressmagazine Com Stuffed Mushrooms Science For Kids Life Cycles
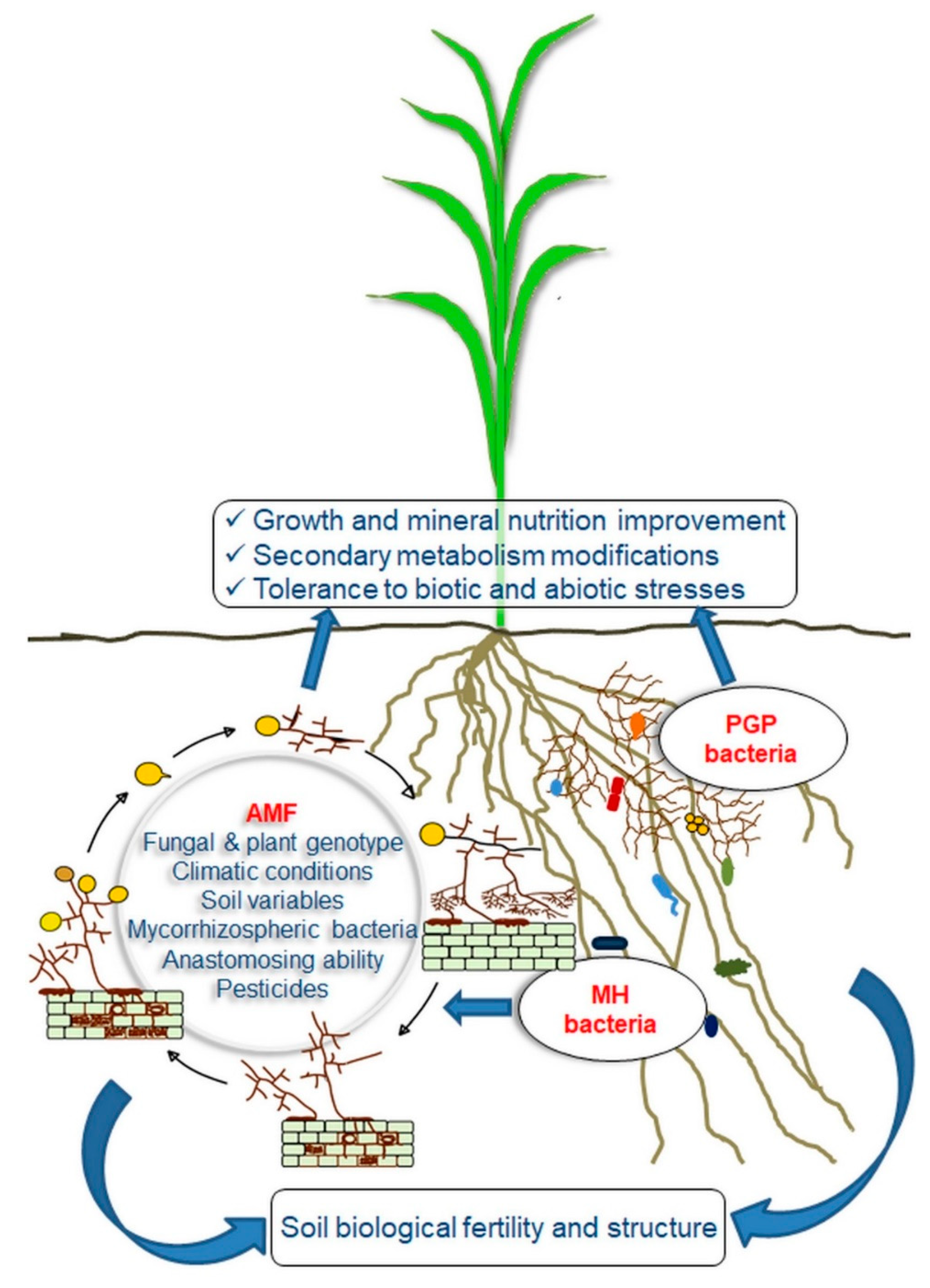
Agronomy Free Full Text Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi And Associated Microbiota As Plant Biostimulants Research Strategies For The Selection Of The Best Performing Inocula Html

Life Cycle Of A Macrocyclic Heteroecious Rust A Mature Diploid Download Scientific Diagram
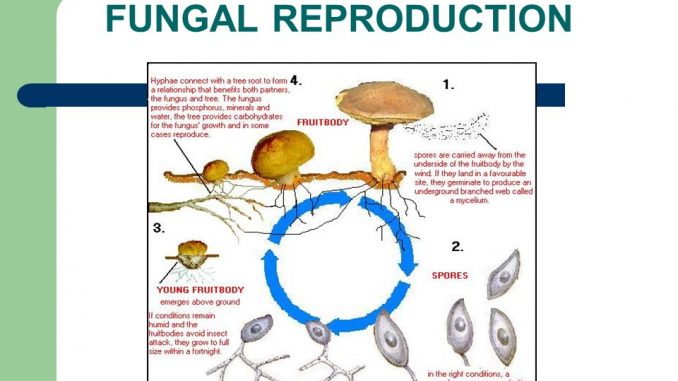
Reproduction In Fungi Asexual And Sexual Methods Online Biology Notes

Life Cycle Of The Ascomycota Download Scientific Diagram

Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Conducting The Hyphosphere Bacterial Orchestra Trends In Plant Science